London Book Fair Announces New Venue
There is a sense of change in the air, and also a sense of deja vue. The London Book Fair has...
There is a sense of change in the air, and also a sense of deja vue. The London Book Fair has...
Dar al-Saqi has announced the withholding of the Mai Ghoussoub Prize for the Novel in its fourth...
2026 IPAF Shortlist Celebrates the Diversity and Questions of Arabic Narrative The International...
The Frankfurt Book Fair has announced the appointment of Joachim Kaufmann as its next president...
As we start 2026 we have picked some exciting books that will be published this year which should...
With the arrival of winter, it is not only the weather that changes, but the rhythm of life...
As 2025 ended, the publishing industry stands at a moment of reflection and reassessment, not as a...
On his birth anniversary on January 6, the name of Gibran Khalil Gibran returns to the cultural...
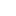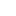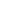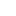
A powerful book of images of Gaza’s children has been published by Scottish independent children’s...
A powerful book of images of Gaza’s children has been published by Scottish independent children’s...
Jamila Hassoun: children’s inability to access books motivated me to provide them Moroccan...
Meeting the Big Bad Wolf himself. Malaysia’s Andrew Yap The Malaysian bookseller snappily called...
The Eyes of Gaza: A Diary of Resilience by Plestia Alaqad Plestia Alaqad is an award-winning...
What You are Looking For is in the Library focuses on a mysterious librarian who helps individuals...
In the literary worlds crafted by Japanese author Yoko Ogawa, grief is never a fleeting emotion or...
IBBY Congress, Italy From August 30, 2024 to September 1, 2024 Website:...
Emirates Airline Festival of Literature Jan 29-Feb 2, 2025 The Emirates Airline Festival of...
International Publishers Congress 4-6 December Website:...
Più Libri Più Liberi, Italy 4 – 8 December Più libri is the first Italian fair dedicated...
Paraty International Literary Festival (FLIP), Brazil...
FIL de Guadalajara, Mexico 30 November – 8 December...
Salon du livre de Montréal, Canada 27 November – 1 December ...
Baku Book Fair, Azerbaijan 20 – 24 November...